Drought Central, Drought Observatory by CNR IBE
Drought Situation
Some content are available only in Italian
- Ramona Magno
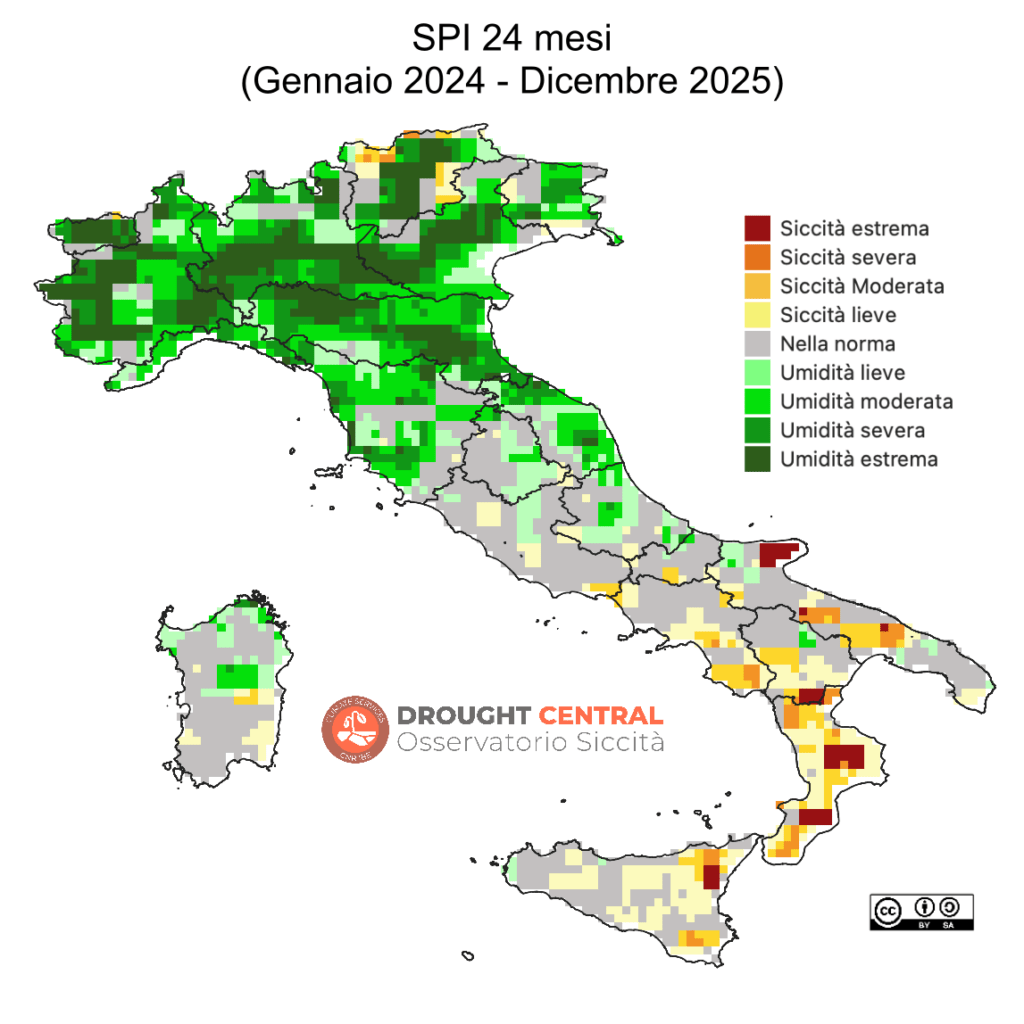
- Gli apporti nevosi, in termini di Equivalente Idrico Nivale (SWE) a livello nazionale nella prima decade di Gennaio 2026, indicano valori sotto la mediana del periodo 2011-2024 nonostante le nevicate di questo inizio anno. Al nord la zona che sta soffrendo maggiormente è quella orientale (-68% nel bacino dell’Adige), così come alti sono i deficit sugli Appennini meridionali (CIMA Foundation).
- Invasi: Nonostante le precipitazioni abbiano portato ad un generale incremento dei livelli, permangono le criticità negli invasi meridionali e delle isole maggiori (vedi mappe).
- Grandi laghi del nord Italia: Dopo la prima settimana di Gennaio il lago Maggiore e il Garda si mantengono su livelli leggermente superiori alla media, il lago di Como ha un andamento altalenante, ma attorno alla media, mentre l’Iseo continua la sua ripida discesa ben al di sotto della norma, con un riempimento pari al 24%.
Previsioni per i prossimi mesi
Per quanto riguarda le temperature dell’aria del trimestre Febbraio-Aprile 2026, i dati d’insieme dei maggiori centri europei per le previsioni a medio termine danno un segnale positivo pressochè su tutta Europa, ma con le probabilità più alte sulla porzione centrale e sulle regioni Mediterranee. Anomalie positive sono previste anche per le temperature superficiali del Mar Mediterraneo (probabilità 70-100%). Per quanto riguarda le piogge, invece, la previsione non risulta sufficientemente robusta per dare un segnale di surplus o deficit chiaro su quasi tutta l’Europa. Tuttavia, il centro di previsioni a medio-lungo termine ECMWF indica un segnale di deficit fra Inghilterra, Nord della Francia e Germania (con probabilità 40-50%) e surplus sul Mediterraneo (probabilità 40-50%).Drought WebGIS
A WebGIS application based on open source solutions customized to integrate different datasets and share maps and graphs of drought indices with researchers, decision-makers and other stakeholders.
Different functions allow to select sections of territory or visualize the trend of the indices in a specific pixel.
Maps and graphs can also be downloaded in png format.
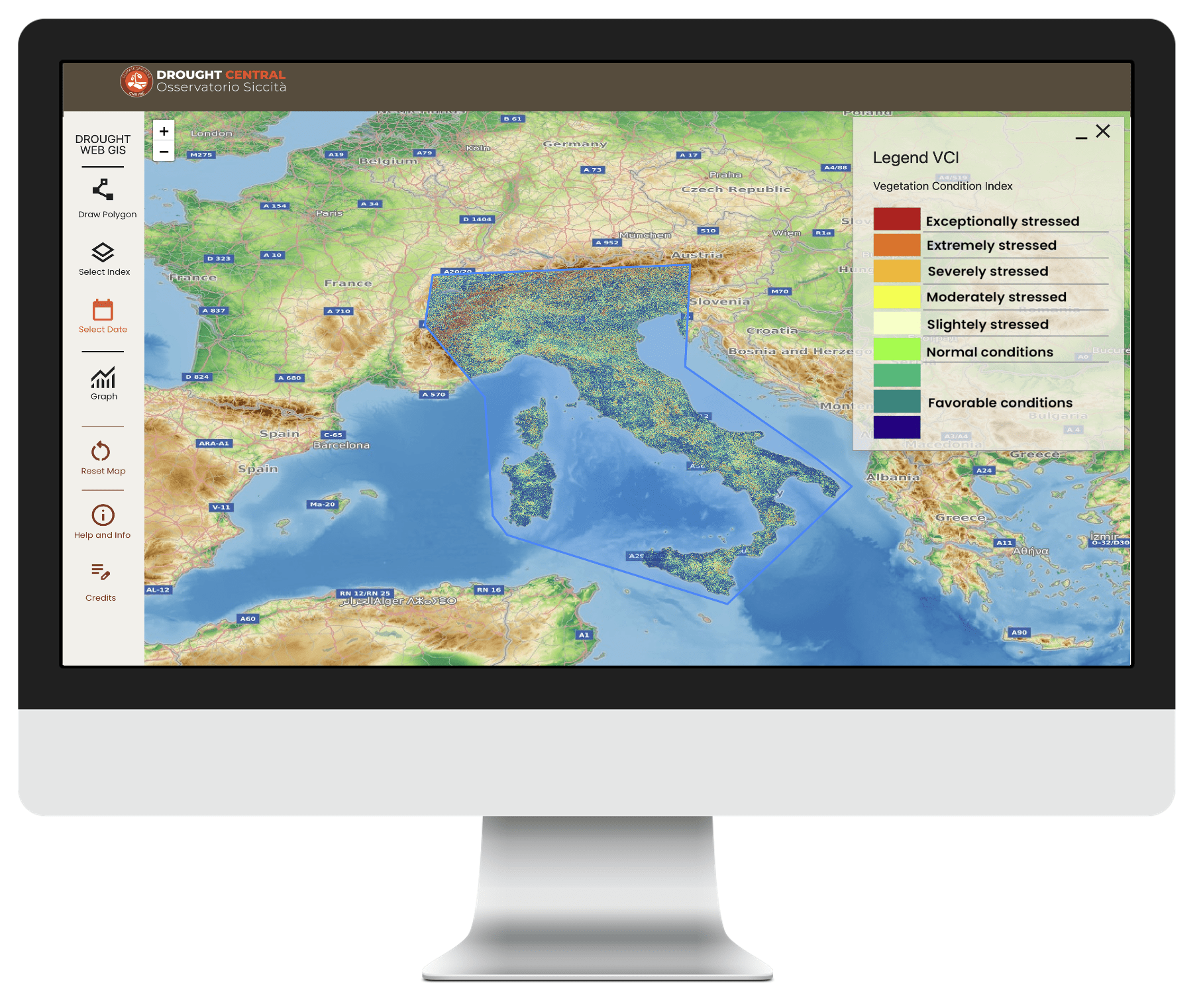
Please Note: due to problems concerning the Terra MODIS satellite, the TCI and VHI indices are available until the 9th of November 2022. They will be replaced soon with new products.
Please Note: Due to the size of the images, it is possible to download sections of the vegetation indices smaller than the whole geographic window.
Drought Scan
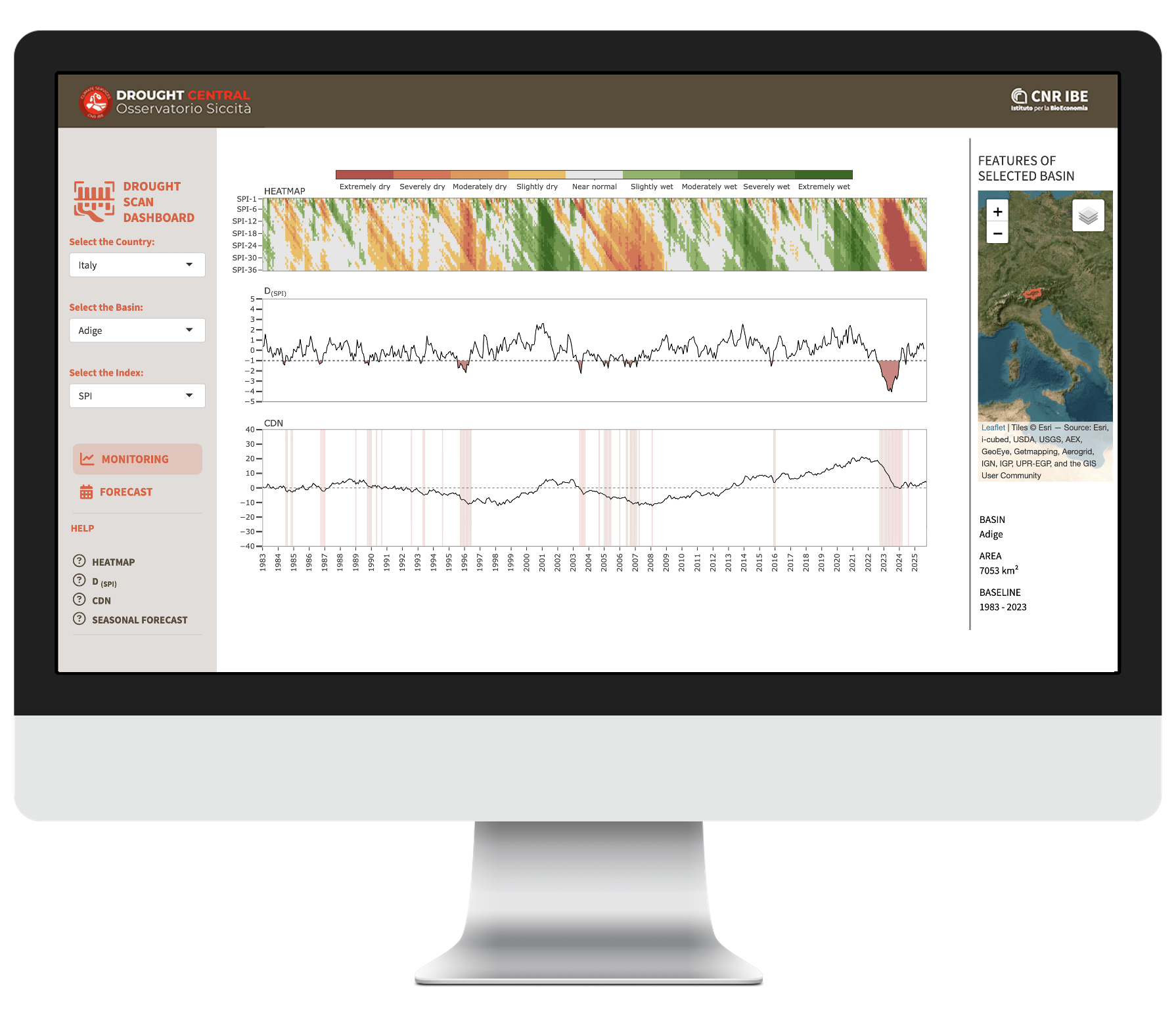
The Drought Scan (DS) is an operational climate service for users with different profiles — technicians, researchers, irrigation consortia, and water authorities — who need a clear, consistent, and scalable assessment of drought conditions at the river-basin scale, using tools that are easy to use yet scientifically robust.
For further information, visit the dedicated page.

Drought
is a complex phenomenon
The challenge
Increasing environmental resilience
A Scientific Proactive approach
Technical support and timely information
A frequent phonomenon
After flooding, it is the second natural disaster that affects the population.
Long term impact
The impact on the environment and human activities can show up late and persist even after the end of the drought event.
High variability
Its intensity and spatial extent are extremely variable.
A creeping phenomenon
With respect to other natural extreme events, drought is characterised by a slow and often difficult to define onset and a long-lasting evolution.
Drought Observatory: the reason why

Drought monitoring and forecasting system
Integration of ground-based and satellite data
The Indices: Drought occurrences and trends
- direct climate-based indices.
- indirect vegetation-based indices

Spatial Data Infrastructure
SOA | OGC | PostgreSQL
A Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) based on Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) standards. Database-centred architecture, with PostgreSQL DataBase Management System.
Innovative Approach
The geographic data flows (from the download of remote sensing and climatic data to the storage of final indices) and all the related geoprocessing functions are integrated in a single environment.
Advanced Statistical Procedures
The integration of the PL/R (R Procedural Language) wrapper into the procedural language of PostgreSQL (PL/pgSQL) allowed the creation of advanced statistical procedures using R engine.