Drought Central, Drought Observatory by CNR IBE
Drought Situation
Some content are available only in Italian
- Ramona Magno
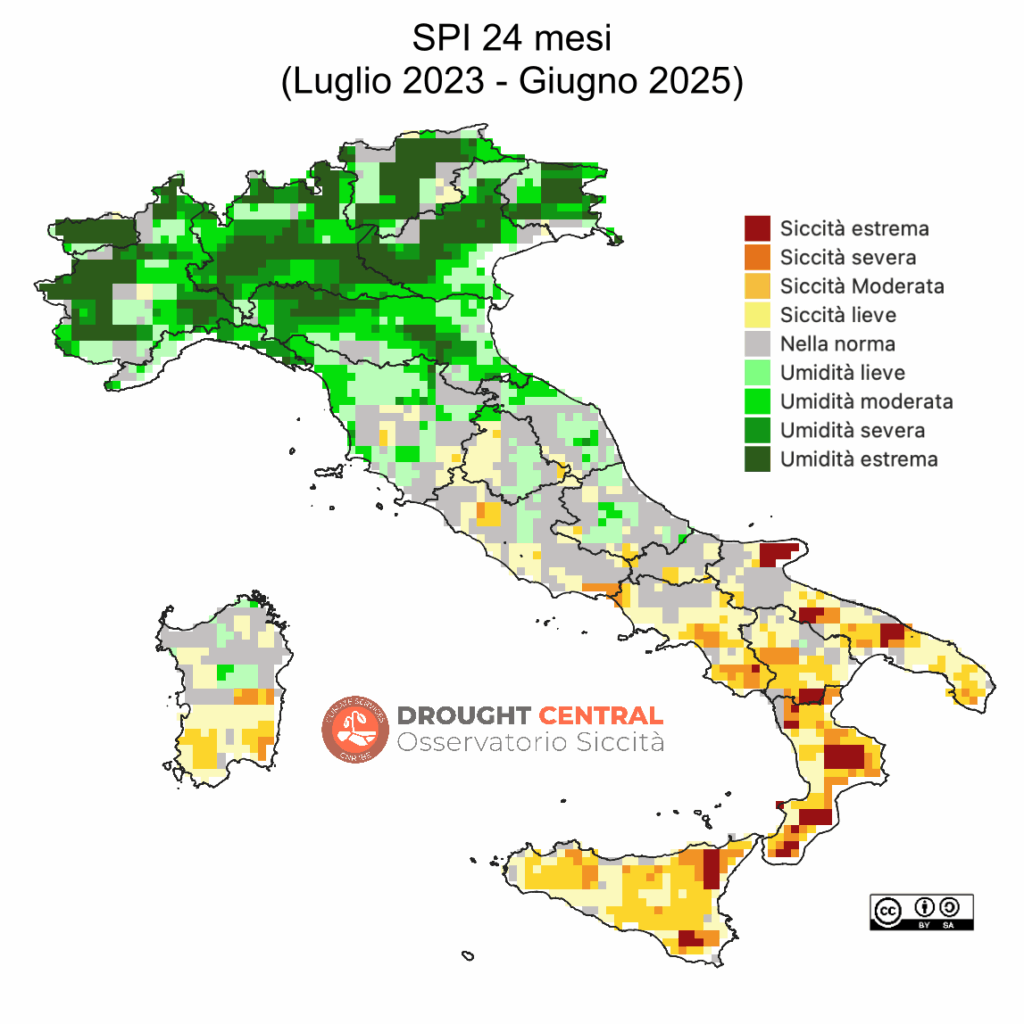
- Invasi: I singoli invasi hanno comportamenti diversi a seconda delle zone, con volumi compresi fra il 23% e il 56% rispetto al totale di regolazione. Tuttavia in Puglia e Basilicata si registra la situazione peggiore (vedi mappe dei principali invasi).
- In merito ai grandi laghi del nord Italia, all’8 Luglio 2025, i valori di riempimento sono al di sotto della media per i laghi Como e Iseo, in media il Maggiore e sopra media il Garda.
- La produzione di energia idroelettrica in Sicilia nella settimana fra il 23-29 Giugno si mantiene al terzo valore più basso degli ultimi 10 anni, ma ben al di sopra del 2024.
Previsioni per i prossimi mesi
Per quanto riguarda le temperature dell’aria del trimestre Agosto-Ottobre 2025, i dati d’insieme dei maggiori centri europei per le previsioni a medio termine prevedono valori sopra la media su tutta Europa con una probabilità del 70-100% praticamente ovunque. Stessa probabilità anche per le temperature superficiali del Mar Mediterraneo che dovrebbero restare al di sopra della media per tutto il trimestre. Per quanto riguarda le piogge, la previsione indica, con probabilità del 40-50% periodi più secchi sull’Europa orientale, già colpita da una lunga e intensa siccità, e sulla penisola Iberica. In media il resto dei Paesi, compresa l’Italia.Drought WebGIS
PLEASE NOTE: The WebGIS is currently offline as we are updating the user interface. It will be accessible again by the end of August.

Drought
is a complex phenomenon
The challenge
Increasing environmental resilience
A Scientific Proactive approach
Technical support and timely information
A frequent phonomenon
After flooding, it is the second natural disaster that affects the population.
Long term impact
The impact on the environment and human activities can show up late and persist even after the end of the drought event.
High variability
Its intensity and spatial extent are extremely variable.
A creeping phenomenon
With respect to other natural extreme events, drought is characterised by a slow and often difficult to define onset and a long-lasting evolution.
Drought Observatory: the reason why

Drought monitoring and forecasting system
Integration of ground-based and satellite data
The Indices: Drought occurrences and trends
- direct climate-based indices.
- indirect vegetation-based indices

Spatial Data Infrastructure
SOA | OGC | PostgreSQL
A Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) based on Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) standards. Database-centred architecture, with PostgreSQL DataBase Management System.
Innovative Approach
The geographic data flows (from the download of remote sensing and climatic data to the storage of final indices) and all the related geoprocessing functions are integrated in a single environment.
Advanced Statistical Procedures
The integration of the PL/R (R Procedural Language) wrapper into the procedural language of PostgreSQL (PL/pgSQL) allowed the creation of advanced statistical procedures using R engine.